SmartX Halo P Series Appliance HCI Solution Using Optane PMEM in App Direct Mode to Achieve Low Latency
Built with company's software SMTX OS, reaches 1.2 million IO/s, 25GB bandwidth, while latency at application side below 100μs.
This is a Press Release edited by StorageNewsletter.com on July 3, 2020 at 2:27 pmSmartX, Inc. announced its low-latency HCI solution and Halo P series appliance built with the company’s core software SMTX OS and Intel Optane persistent memory (PMEM).
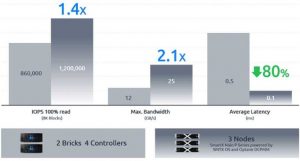
The company has applied PMEM with App Direct mode as a key component in HCI solution. At the same time, with end-to-end optimizations across computing virtualization, storage network as well as storage medium, the solution obtains performance as well as low-latency server virtualization storage based on limited computing resources. During the test, only 3-node Halo P series appliance is applied to reach 1.2 million IO/s, 25GB bandwidth, while the latency at the application side keeps below 100μs.
SMTX OS components
With stability and features, the HCI solutions from the firm have been applied to the production environments in banking, securities, insurance, funding as well as other financial verticals. However, some clients are hesitated to replace their bare metal servers and AFA with HCI solution, over the concerns of the performance and latency of computing virtualization, networking and storage layers. To solve this problem, the company started a project with the code name ‘Sailfish’ (the fastest fish in the ocean) since 2019, with App Direct mode for cache acceleration and optimized the company’s HCI core software SMTX OS.
PMEM adds a storage tier between memory and SSDs, which has memory-like high performance with low latency, durability and reliability, data persistency, as well as byte-addressable. Configured in App Direct mode, the applications are able to access the data in persistent memory of PMEM.
To fully leverage the capabilities of PMEM, the firm has made end-to-end optimization across computing virtualization, storage network, and storage medium. Due to the specific architecture of HCI, the performance enhancement can only be achieved with limited computing resources, which has brought with many challenges for the Sailfish project.
To counter those difficulties, the company has made improvements from the following perspectives.
-
At the storage layer, the firm leverages the low latency and persistent memory of PMEM App Direct mode to save the most frequently accessed data in the cluster. In order to ensure the reliability and HA of the data, the data cached in PMEM will also be replicated to the other nodes. Also SMTX OS takes advantage of the byte-addressable feature of persistent memory to redesign the journal, effectively solving the problem of write amplification. Through the DMA method, the data copy tasks between the memory and the persistent memory are transferred to the hardware, improving the efficiency of memory copy, so as to enhance the storage performance, without generating additional CPU resource requests.
-
At the computing virtualization layer, the storage virtualization is devolved from the VM to the storage software stack, through the SMTX ELF boost mode to avoid additional performance overhead caused by IO requests passing through the VMs. At the same time, the memory is shared by the VM and the storage system to avoid memory replication on the IO path.
-
At the storage network layer, RDMA over Converged Ethernet (RoCE) is used to accelerate network IO requests. The implementation of the network protocol is transferred to the network card. Hardware acceleration function of the network card is leveraged to reduce the distributed storage performance overhead during network communications.
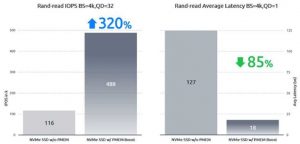
With the above optimizations, the VM’s IO performance has been enhanced by 320%, while latency reduced by more than 85%.
Click to enlarge
So far, the technologies used in Sailfish project have been integrated into the Halo P series appliance. This series appliance is capable of mission-critical applications such as transaction databases and MLs with demanding requests on IO. In addition, with higher performance, the appliance also increases the density of VMs to simplify IT deployment and reduces TCO. Currently, it has been tested and implemented in the financial industry.
Compared with a mainstream mid-to-high-end AFA in the market, the 8KB random read performance of the 3-node Halo P series appliance reaches 1.2 million IO/s, which is 1.4 times that of the AFA. The sequential read bandwidth reaches 25GB, 2.1 times of AFA. The application side latency is 100μs, while the latency of the AFA at controller end reaches 500μs already. Moreover, the appliance keeps the simplicity and resilience of HCI architecture, as well as the highly competitive TCO compared with mid-to-high level AFAs.
Click to enlarge
“SmartX has been committed to building the most excellent HCI infrastructure,” according to Kyle Zhang, co-founder and CTO. ”In the Sailfish project, we provide the best practice in adopting PMEM in HCI solutions. From the test results, we have seen that the introduction of new storage technologies can greatly improve the performance of HCI system and address the real-workload challenges for critical applications. In the future, SmartX will collaborate with Intel and other leading industry leaders to introduce more advanced technologies to lead the next-level innovations in HCI.”


















 Subscribe to our free daily newsletter
Subscribe to our free daily newsletter


