History (1988): U.C. Berkeley Paper Catalyses Interest in RAID
Outperforming mainframe drives
This is a Press Release edited by StorageNewsletter.com on May 17, 2018 at 2:00 pmThis article comes from the Computer History Museum.
1988: U.C. Berkeley paper catalyses interest in RAID
Redundant Arrays of Independent Disks outperform mainframe drives
The First Raid Group (1984)
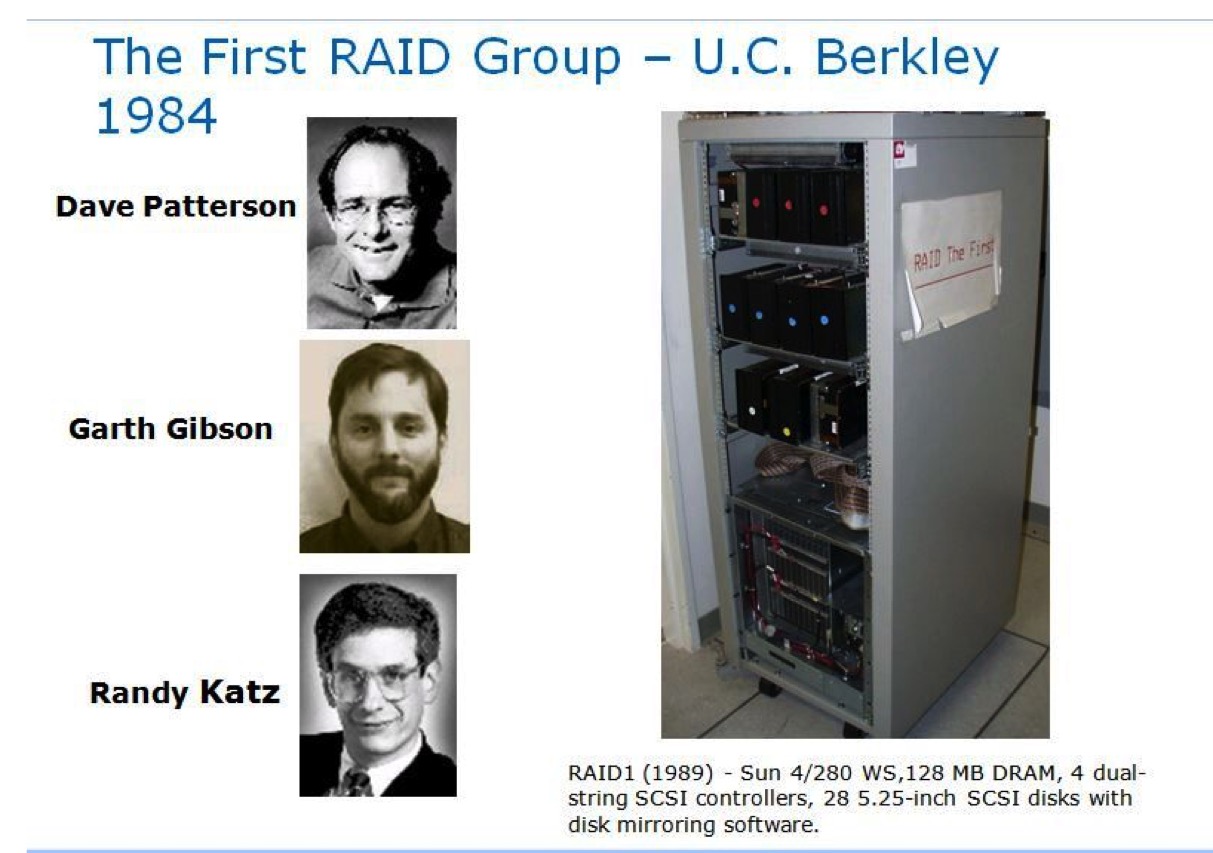
(© Microsoft)
Editor: Note that, in the image above coming from the Computer Museum, the picture of Garth Gibson is wrong. He is the good one:

David Patterson, Garth Gibson, and Randy Katz of U.C. Berkeley presented the paper A Case for Redundant Arrays of Inexpensive Disks (RAID) in 1988 claiming that an array of multiple inexpensive disks intended for PC applications could outperform single, large expensive mainframe drives.
The concept of mirroring was already well known and some storage systems had already been constructed around arrays of small disks, however their acronym (later changed to Redundant Array of Independent Disks) catalyzed interest in the approach and attracted commercial suppliers.
Pioneering work that led to RAID includes disk-mirrored storage by Tandem Computers in its Non-Stop Architecture and subsystem-mirrored RA8X disk drives (now known as RAID Level 1) by DEC in its HSC50 and HSC 70 systems in the early 1980s.
Thinking Machines’ DataVault used error-correction codes (RAID-2) in an array of disk drives. The IBM 353 drive used a similar approach in the early 1960s.
Patent applications by IBM engineers, Norman Ken Ouchi (1977) and Brian Clark et. al. (1988) disclosed techniques employed in subsequent versions of RAID.
Early independent RAID vendors include Adaptec and Array Technology that was founded in 1987 and acquired successively by Seagate, Tandem, and EMC.
A number of standard schemes, called levels, each with many variations, have evolved.
RAID levels and their associated data formats are standardized by the Storage Networking Industry Association (SNIA) in the Common RAID Disk Drive Format (DDF) standard.
Today, most server-and networked-based storage is based on RAID, and many PC users employ hardware or software RAID systems on their own machines.













 Subscribe to our free daily newsletter
Subscribe to our free daily newsletter

