R&D: Efficient Sequential Data Migration Scheme Considering Dying Data for HDD/SSD Hybrid Storage Systems
Proposed scheme can perform better than existing data migration schemes not aware of dying data under various benchmarks.
This is a Press Release edited by StorageNewsletter.com on November 22, 2017 at 2:29 pmIEEE Access as published an article written by Mingwei Lin, College of Mathematics and Informatics, Fujian Normal University, Fuzhou, China, Riqing Chen, Institute of Big Data for Agriculture and Forestry, Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, Fuzhou, China, Jinbo Xiong, Xuan Li, and Zhiqiang Yao, College of Mathematics and Informatics, Fujian Normal University, Fuzhou, China.
Transitions between live, dead, and dying states
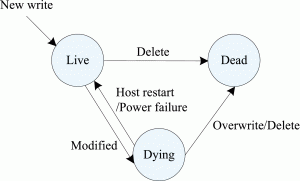
Abstract: “Because the solid-state drive (SSD) shows high access performance, it is usually integrated into existing hard disk drive (HDD)-based storage hierarchy to form HDD/SSD hybrid storage systems. To further improve the performance of HDD/SSD hybrid storage systems, data migration schemes have been put forward to migrate the sequential data between HDD and SSD. However, the existing schemes cannot be aware of dirty data in the buffer and then incur a large number of unnecessary page migrations. In this paper, we devise an efficient data migration scheme considering dying data for HDD/SSD hybrid storage systems. In this scheme, a new liveness state, called the dying state, is utilized to identify the live data, which will become dead shortly due to its corresponding dirty version in the buffer. To decrease the page migration count, this scheme uses the benefit-to-cost ratio to select a block for data migration and copies the up-to-date version of dying data into the free space instead of migrating the dying data. Our experimental results show that our proposed scheme can perform better than existing data migration schemes that are not aware of dying data under various benchmarks.“













 Subscribe to our free daily newsletter
Subscribe to our free daily newsletter

