Attala Systems: 1PB/U Density Spark and Lustre Storage Solution for HPC
With Intel and Supermicro
This is a Press Release edited by StorageNewsletter.com on November 23, 2017 at 2:35 pmAttala Systems, Inc. announced its storage solution for the HPC market at Super Computer 2017 in Denver, CO.
The solution, which will be available in 2018, was developed in collaboration with Intel Corp. and Super Micro Computer, Inc. and utilizes Attala’s Composable Storage Infrastructure and management software, Supermicro enclosures, Intel FPGAs and Optane and 3D NAND SSDs with NVMe to achieve 5.5 million IO/s and 1PB per 1U of rack space.
Attala Composable Storage Infrastructure
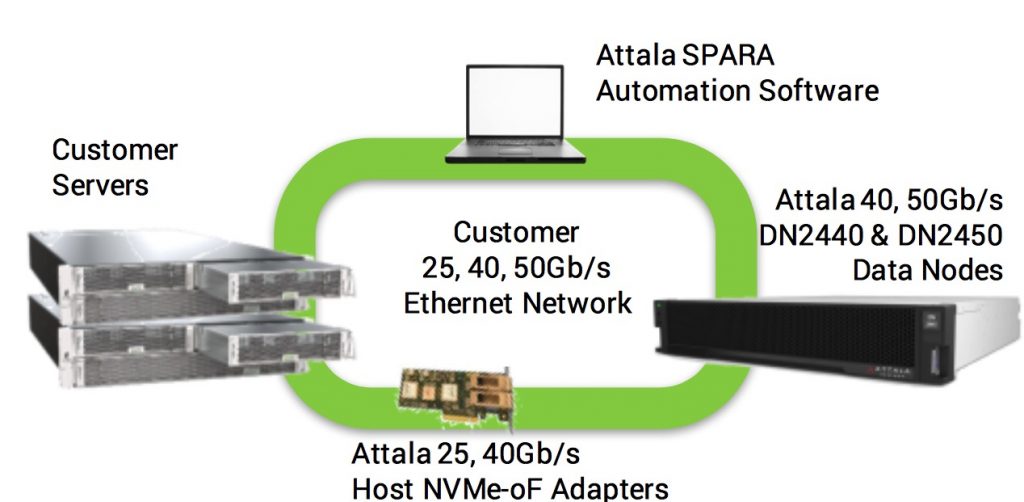
It also provides multi-tenancy and parallel data sharing capabilities for Lustre and Apache Spark.
Attala, which recently won the G2M Research Most Innovative NVMe AFA Key company Award for Fall 2017, was demonstrating the solution with Spark in both the Intel booth, and with Lustre in the Supermicro booth at SC17.
“Simultaneously achieving high density and performance in an HPC storage system – that can be reliably shared by multiple users – has always been a challenge, especially at a competitive price point,” said Taufik Ma, CEO, Attala. “Our demonstrations at SC17 are meant to show not only that these attributes aren’t mutually exclusive, but that they can be achieved with real HPC workloads such as Lustre and Spark. This level of density and performance opens up new options for HPC users.”
Historically, HPC storage systems have either focused on achieving high density or high performance, but not both. Additionally, high-performance HPC storage sulutions have generally not been available at competitive price points. The HPC solution from Attala changes that paradigm, and does so for real HPC workloads.
When the solution is available in 2018, each 1U storage node will feature up to 1PB capacity, 5.5 million IO/s, and multi-path network redundancy. The reduction in latency provided by composable storage infrastructure also turbocharges small-packet performance in systems such as Lustre’s Data-on-MDT feature. Finally, the solution allows multi-tenancy storage operations and parallel data sharing in HPC applications.
“We are excited by the many possibilities that Intel Optane technology can enable for HPC, especially when solutions are built to take advantage of the unique and revolutionary nature of the technology,” said Bill Leszinske, VP and director of strategic planning, marketing and business development for of Intel’s non-volatile memory solutions group. “Combining the high throughput, low latency and very high endurance of Intel Optane technology with Intel 3D NAND SSDs and Intel FPGAs opens the door for high-performance, high density petabyte-scale storage solutions.“
“Supermicro has been a longtime key player in the HPC market,” said Tau Leng, PhD, SVP of technology and marketing, Supermicro. “This demonstration shows that the combination of Supermicro’s wide offering of NVMe-capable server and storage solutions, Attala’s high-performance composable storage infrastructure, and Intel SSD and Intel FPGA technology can fundamentally change the game for HPC storage, giving HPC users new options for their workloads.”
The HPC-focused solution utilizes the FPGA-powered Attala HNA25/40 Host NVMe-oF adapters in host servers and Attala NSC40/50 NVMe-oF system controllers and Intel NVMe SSDs in a Supermicro SSG-136R-N32JBF 1U enclosure.
Because the Attala storage nodes do not require a CPU, host agents or software, they simplify deployment and maintenance of the overall solution across multiple racks and heterogeneous environments. Storage provisioning and orchestration are also simplified thanks to Attala’s SPARA management software, which automates the management and use of storage assets. These capabilities help reduce the cost of the overall solution, enabling performance and storage density to be achieved in an HPC storage system with competitive acquisition costs and TCO.
Read also:
Start-Up Profile: Attala Systems
In storage and networking infrastructure based on use of FPGAs and cloud-focused self-learning orchestration and provisioning software
by Jean Jacques Maleval | 2017.08.11 | News













 Subscribe to our free daily newsletter
Subscribe to our free daily newsletter

