Molecular Storage from Seoul National University
More efficient data retrieval from synthetic polymer storage
This is a Press Release edited by StorageNewsletter.com on November 8, 2024 at 2:00 pmIncreasing amounts of data require storage, often for long periods. Synthetic polymers are an alternative to conventional storage media because they maintain stored information while using less space and energy.
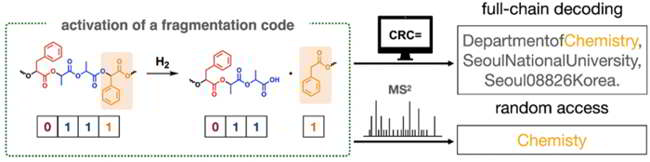
Demonstrated shotgun sequencing of 512 repeating unit sequence-defined polymers with a molecular weight (57.3 kDa) far exceeding the analysis limit of mass spectrometry. Chemically activated fragmentation code was employed to generate MS-compatible oligomers. Shotgun sequencing also allowed random access to the stored information.
(© Wiley-VCH, with credit to ‘Angewandte Chemie’)
However, data retrieval by mass spectrometry limits the length and thus the storage capacity of individual polymer chains. In the journal Angewandte Chemie, researchers have now introduced a method that overcomes this limitation and allows direct access to specific bits without reading the entire chain.
Data accumulates constantly, resulting from business transactions, process monitoring, quality assurance, or tracking product batches. Archiving this data for decades requires much space and energy. For long-term archival of large amounts of data that requires infrequent access, macromolecules with a defined sequence, like DNA and synthetic polymers, are an attractive alternative.
Synthetic polymers have advantages over DNA: simple synthesis, higher storage density, and stability under harsh conditions. Their disadvantage is that the information encoded in polymers is decoded by mass spectrometry (MS) or tandem-mass sequencing (MS2). For these methods, the size of the molecules must be limited, which severely limits the storage capacity of each polymer chain. In addition, the complete chain must be decoded in sequence, building block by building block – the bits of interest cannot be accessed directly. It is like having to read through an entire book instead of just opening it to the relevant page. In contrast, long chains of DNA can be cut into fragments of random length, sequenced individually, and then computationally reconstructed into the original sequence.
Kyoung Taek Kim and his team at the Department of Chemistry at Seoul National University, Republic of Korea, have developed a new method by which very long synthetic polymer chains whose molecular weights greatly exceed the analytical limits of MS and MS2 can be efficiently decoded. As a demonstration, the team encoded their university address into ASCII and translated this – together with an error detection code (CRC, an established method used to ensure data integrity) – into a binary code, a sequence of ones and zeroes. This 512-bit sequence was stored in a polymer chain made of 2 different monomers: lactic acid to represent a 1 and phenyllactic acid to represent a 0. At irregular intervals, they also included fragmentation codes containing mandelic acid. When chemically activated, the chains break at those locations. In their demonstration, they obtained 18 fragments of various sizes that could be individually decoded by MS2 sequencing.
Specially developed software initially identified the fragments based on their mass and their end groups, as shown by the MS spectra. During the MS2 process, previously measured molecular ions brake down further, and these pieces were then also analyzed. The fragments could be sequenced based on the mass difference of the pieces. With the aid of the CRC error detection code, the software reconstructed the sequence of the entire chain, overcoming the length limit for the polymer chains.
The team was also able to decode interesting bits without sequencing the entire polymer chain (random access), such as the word ‘chemistry’ in the code for their address. By taking into account that the parts of their address are all in a specific order (department, institution, city, postal code, country) and separated by commas they were able to isolate the location where the desired information was stored within the chain and only sequenced the relevant fragments.
Article: Shotgun Sequencing of 512-mer Copolyester Allows Random Access to Stored Information
Angewandte Chemie has published an article written by Heejeong Jang, Hyunseon Chu, Hyojoo Noh, and Prof. Kyoung Taek Kim, Department of Chemistry, Seoul National University, Seoul, 08826 Korea
Abstract: “Digital information encoded in polymers has been exclusively decoded by mass spectrometry. However, the size limit of analytes in mass spectrometry restricts the storage capacity per chain. In addition, sequential decoding hinders random access to the bits of interest without full-chain sequencing. Here we report the shotgun sequencing of a 512-mer sequence-defined polymer whose molecular weight (57.3 kDa) far exceeds the analytical limit of mass spectrometry. A 4-bit fragmentation code was implemented at aperiodic positions during the synthetic encoding of 512-bit information without affecting storage capacity per chain. Upon activating the fragmentation code, the polymer chain splits into 18 oligomers, which could be individually decoded by tandem-mass sequencing. These sequences were computationally reconstructed into a full sequence using an error-detection method. The proposed sequencing method eliminates the storage limit of a single polymer chain and allows random access to the bits of interest without full-chain sequencing.“













 Subscribe to our free daily newsletter
Subscribe to our free daily newsletter

