IEDM 2024: Kioxia to Unveil Emerging Memory Technologies
DRAM utilizing oxide semiconductors with focus on reducing power consumption, MRAM suitable for larger capacities for SCM application, and novel structure of 3D flash memory with superior bit density and performance
This is a Press Release edited by StorageNewsletter.com on October 30, 2024 at 2:01 pmKioxia Corp. announced that the company’s research papers have been accepted for presentation at IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM) 2024, an international conference to be held in San Francisco, CA, USA, December 7-11.
The company is committed to the R&D of semiconductor memory, which is indispensable for the advancement of AI and the digital transformation of society. Beyond its 3D flash memory technology BiCS FLASH, the firm excels at research in emerging memory solutions. It is constantly striving to meet the needs for future computing and storage systems with innovative memory products.
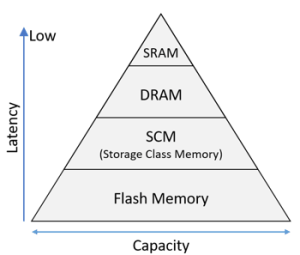
Existing computing systems leverage DRAM, a primary memory device enabling CPU to process data swiftly, alongside flash memory for the storage of extensive data. Kioxia is spearheading R&D for Storage Class Memory (SCM), a memory solution positioned between DRAM and flash memory in the semiconductor memory hierarchy, designed to handle larger data volumes than DRAM and at higher speed than flash memory.
At IEDM, the company will unveil technologies tailored to each of these 3 semiconductor memory layers: (1) a new type of DRAM utilizing oxide semiconductors with a focus on reducing power consumption, (2) MRAM suitable for larger capacities for SCM application, and (3) a novel structure of 3D flash memory with superior bit density and performance.
Emerging memory technologies:
1. Oxide-semiconductor channel transistor DRAM (OCTRAM): This technology was jointly developed by Nanya Technology Corp. and Kioxia. The companies developed a vertical transistor that enhances circuit integration by improving the manufacturing process. The companies achieved extremely low current leakage by bringing out the properties of the transistor using an oxide-semiconductor. This can potentially lower power consumption in a wide range of applications, including AI and post-5G communication systems, and IoT products.
Paper title: Oxide-semiconductor Channel Transistor DRAM (OCTRAM) with 4F2 Architecture (Paper Number: 6-1)
2. High-capacity crosspoint MRAM technology: This technology was jointly developed by SK hynix Inc. and Kioxia. With this technology, the companies achieved cell RW operation at the smallest-ever scale of cell half-pitch of 20.5 nanometers for MRAM by combining cell technology that pairs selectors suitable for large capacities with magnetic tunnel junctions, and applied fine processing technology for crosspoint-type arrays. Memory reliability tends to degrade as cells are miniaturized. The companies developed a potential solution by utilizing a new readout method that leverages the transient response of selectors and by reducing the parasitic capacitance of readout circuits. This technology has practical applications for AI and big data processing.
Paper title: Reliable memory operation with low read disturb rate in the world smallest 1Selector-1MTJ cell for 64 Gb cross-point MRAM (Paper Number: 20-1)
3. Next-Gen 3D memory technology with horizontal cell stacking structure: Kioxia developed a new 3D structure to improve reliability and prevent degradation of NAND-type cell performance. Degradation of performance typically occurs when the number of stacked layers increases in conventional structures. This structure arranges NAND-type cells horizontally by stacking them compared to the conventional structure of vertically arranging NAND-type cells. This structure allows for the realization of 3D flash memory with high bit density and reliability at low cost.
Paper title: Superior Scalability of Advanced Horizontal Channel Flash For Future Generations of 3D Flash Memory (Paper Number: 30-1)
Under its mission of ‘uplifting the world with ‘memory’, Kioxia aims to pioneer a new era with memory technology and will continue to promote research and technological development to support the future of digital society.















 Subscribe to our free daily newsletter
Subscribe to our free daily newsletter

