Highpoint NVMe Adapter to Maximize Potential of Storage Infrastructure
Enhancing performance, increasing capacity, and ensuring data reliability to range of platform and applications
This is a Press Release edited by StorageNewsletter.com on July 11, 2024 at 2:01 pm
- NVMe storage flexibility: NVMe Adapters, such as HighPoint Technologies, Inc.’s Rocket 7600/1600 families, are specialized solutions intended for server or industrial applications. They are commonly used in data centers and edge server environments to support large configurations of 2.5” NVMe storage media, offering capacities up to 60TB.
- Types of NVMe adapters: NVMe adapters include Switch adapters, like the Broadcom P411W-32P, which support multiple NVMe SSDs using PCIe Switching technology, and RAID adapters, like the Rocket 7628A, which add RAID capabilities. Switch adapters enable Hot-Swap/Hot-Plug, while RAID adapters support multiple RAID arrays and advanced management features.
- Enterprise Applications: Primarily used in data centers, edge servers, and industrial applications, NVMe adapters support large configurations of 2.5” NVMe SSDs, offering high storage capacities up to 60TB. They are for data-intensive applications requiring performance and reliability.
- Benefits: NVMe adapters provide flexibility in storage configurations, high capacities, robust connectivity, and low power consumption. They adhere to strict industry standards, ensuring compatibility with various server and workstation platforms.
- Use Cases: NVMe adapters excel in high-speed data ingestion, processing, and storage archiving, making them suitable for AI training, ML, and scientific simulations. They enhance performance and reliability in data-intensive environments like cloud storage and automotive systems.
HighPoint Technologies, Inc. explores how an NVMe adapter can maximize the potential of storage infrastructure by enhancing performance, increase capacity, and ensure data reliability to a range of platform and applications.
Why Choose NVMe adapter?
NVMe storage solutions are available in a multitude of form factors, ranging from individual SSDs and pocket drives to external enclosures and PCIe controller cards.
Outside of single-SSD upgrades, NVMe controller cards are the most common. Most are likely already familiar with NVMe AICs – this type of device enables you to add anywhere from 1 to 8 M.2 SSDs via PCIe connectivity. Most are marketed as accessories for a particular model or brand of computing platform, or motherboard. Common examples include Asus’s Hypercards and Dell Ultra Speed controllers. These types of solutions support between 1 and 4 SSDs, largely function as simple upgrades, and are usually classified as ‘expansion cards’. They provide additional M.2 ports, and not much else. Some advanced solutions provide more features, such as the HP Z Turbo Drive, which is available with RAID capability, or HighPoint Technologies, Inc.’s Rocket 7608A PCIe Gen5 x16 NVMe AIC, which provides advanced RAID-0, -1 and -10 support in addition to 8 independent M.2 ports, and PCIe switching architecture.
However, the arguably lesser-known class of PCIe NVMe controller card, the NVMe adapter, is among the most advanced and versatile storage connectivity solutions in today’s marketplace. What is NVMe an adapter?
What is NVMe an adapter?
It is worth mentioning that there is some confusion around the term ‘adapter’. In fact, the term is most commonly used as a general descriptor rather than to denote a particular class of controller card. For example, the basic function of any NVMe controller card could qualify as an adapter – the card enables one type of device (an NVMe SSD) to connect to (or adapt to) another type of device or interface (such as a PCIe slot). This is not the same as an actual NVMe adapter, such as the Broadcom P411W-32P Switch adapter, or HighPoint’s Rocket 7600/1600 adapter families.
NVMe adapters are specialized solutions, and usually intended for server or industrial applications. In fact, they are now most commonly employed by data center and edge server/workstation environments. They are used to support large configurations of 2.5” NVMe storage media – generally 4 to 32 U.2, U.3 or E3.S SSDs via various cabling solutions.
The reason behind the general use-case is pretty straightforward – 2.5” form-factor NVMe SSDs are generally classified as enterprise or datacenter storage media, and are available with up 60TB of capacity; this is comparable to SAS/SATA media and many times larger than today’s densest M.2 SSD. The 2.5” form-factor requires considerably more real estate than M.2 or E1.S media – platforms will need mobile racks or a dedicated storage chassis to host the storage.
Rocket 1628A

Types of NVMe adapters
There are 2 primary classes of NVMe adapter; Switch adapters (like the aforementioned Broadcom P411W-32P, and HighPoint Rocket 1628A), and RAID Adapters (such as the HighPoint Rocket 7628A). To clarify, Both classes of product typically employ PCIe switching architecture – this technology is not exclusive to cards classified as switch adapters.
NVMe switch adapters – this type of NVMe adapter utilizes PCIe switching technology to support 4 or more U.2, U.3 or E3.S NVMe SSDs. PCIe switching architecture enable these device to provide a range of features, such as Hot-Swap/Hot-Plug (ability to add or remove NVMe SSDs without powering down or rebooting the system) and the ability to support multiple SSDs per device port (as many as 8 for a total of 32).
NVMe switch adapters are natively supported by modern OS platforms; this means they require no additional software to operate (neither drivers nor applications). They will be automatically recognized by the host – any connected SSD will be available for immediate use. This can also streamline service and maintenance sessions, as the adapter can remain fully operational during a kernel update or patch as support for their hardware is already embedded directly into the OS itself.
Rocket 7628A

NVMe RAID adapters (a.k.a. Pro-Class) – Often categorized as Pro-Class solutions, this type of NVMe adapter adds RAID technology to the mix. In addition to matching the capabilities of switch adapters NVMe RAID adapters can support one or more RAID arrays comprised of NVMe SSDs; most often RAID-0 or -1 configurations. Some advanced adapters, such as HighPoint Rocket 7628A, can host as many 4 separate arrays, including RAID-10 configurations, and bootable volumes.
NVMe RAID adapters often require unique device drivers and/or software applications to provide a full feature set. However, this also can provide several advantages. Unique drivers can be developed for specific operating systems or workflows, and tuned to maximize reliability and performance, and software suites can implement a host of management and monitoring capabilities that are not provided by the host OS. Rocket 7628A is stand out in this sense – in addition to a series of Graphical and Command-Line based RAID Management interfaces, the adapter includes a complete NVMe Sensor and Environmental Monitoring /Logging solution, which enables administrators to track and analyze power consumption and temperature of each SSD in real time via a series of easy-to-read graphs and line charts. This data is especially useful for applications that require storage capable of operating at peak I/O for extended durations, such as an AI/ML/LLM or hosting solution – the insights provided by the service can be used to optimize storage configurations for performance and reliability by studying SSD behavior during peak I/O. In addition, the adapter provides a host of pre-OS level tools in the form of OOB (out-of-band) management, HII and UEFI support.
Benefits of NVMe adapters
NVMe adapters provide many advantages over other NVMe solutions. The most obvious is the flexibility and massive storage capacity they can provide via a single PCIe slot – the ability to host a wide range of 2.5” NVMe SSD (both in terms of form factor and class), and the huge size of individual SSDs (up to 60TB each). NVMe Adapters can host petabytes of storage vs AICs, which are measured in terabyte (or even gigabyte in some cases).
In addition, as NVMe adapters were designed for enterprise hardware environments, most adhere to very strict industry standard chassis form factor and electrical specifications. They are built to withstand the rigors of 24/7 applications, utilize a compact Low-Profile form factor, and are highly power efficient. They are widely compatible with nearly any modern server or workstation platform, including compact rackmount chassis and industrial platforms that host PCIe devices via riser cards.
Flexible storage connectivity
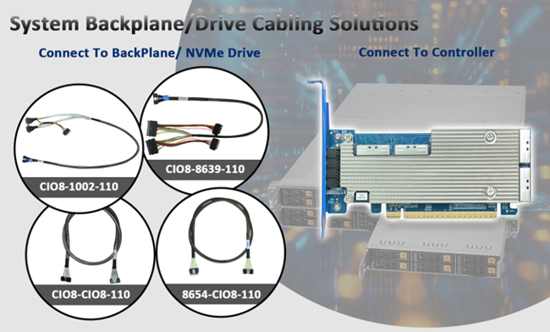
One of the key strengths of an NVMe Adapter is flexibility. The ability to interface with a variety of storage chassis, such as internal 2.5” drive bays, mobile racks, or storage backplanes, enable these solutions to host a wide range of storage configurations. For example, HighPoint’s Rocket 7628A is equipped with 4 MCIO 8i ports, which accept any number of cabling solutions. These include direct to SSD connections such as MCIO to SFF-8639 (U.2/U.3 SSD), and MCIO to SFF-TA-1002 (E3.S SSDs). Options for backplane/mobile rack connectivity are even more diverse: MCIO to MCIO (PCIe Gen5/Gen4 media), MCIO to SFF-8654 (PCIe Gen4 media), MCIO to SFF-8643 (PCIe Gen3 media), and SFF-8612/8611 OCulink (for Gen4 and Gen4 media, respectively).
Ideal for vertical applications
The vast majority of NVMe Adapters are powered by PCIe Switching architecture, which is for applications that need optimal transfer bandwidth and secure, reliable connectivity. Integrated Switch ICs enable these types of solutions to distribute bandwidth internally in order to maximize performance of the upstream and downstream ports. Switch ICs are also engineered to enhance signal clarity to minimize latency and streamline I/O throughput. This approach results in a highly reliable storage solution capable of delivering unparalleled transfer performance, with a high degree of flexibility to boot. NVME adapters enable administrators to fine-tune storage configurations for a wide range of unique projects and workflows.
A prime example is the Rocket 7628A Pro-Class NVMe RAID adapter, which is powered by HighPoint’s PCIe Gen5 switch architecture. Each adapter has x48 lanes of internal PCIe Gen5 bandwidth; by default, x16 lanes are dedicated to the upstream port (connection to the computing platform), and x4 lanes are dedicated to each of the 8 device channels (32 total lanes). This ensures each SSD can perform optimally.
However, bandwidth allocation is not static – it can be redistributed as needed. For example, the adapter can be reconfigured to maximize port connectivity by assigning x1 lanes to 32 individual SSDs.
2.5” NVMe media is also incredibly diverse; both in terms of SSD form factor (U.2, U.3 and E3.S), and in terms of target application. 2.5” NVMe media is available for both enterprise and datacenter applications, up to 60TB in capacity, with specialized sub-categories for applications that require optimal sequential read or sequential write capability, or a balanced approach (solid random + sequential RW performance).
Following table is just a sampling of SSD media supported by NVMe adapters:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Kioxia CD8P-R |
5 |
U.2 |
Datacenter |
19,20 to 30,720GB |
Read Intensive – Sequential Performance |
|
Kioxia CD8P-V |
5 |
U.2 |
Datacenter |
19,20 to 30,720GB |
Mix-Use |
|
Micron 7500Pro |
4 |
U.3 |
Datacenter |
800GB – 15.36TB |
Read Intensive – Sequential Performance |
|
Micron 7500Max |
4 |
U.3 |
Datacenter |
800GB – 15.36TB |
Mixed-use |
|
Kioxia CM7-R |
5 |
U.3 |
Enterprise |
19,20 to 30,720GB |
High-Performance Computing (HPC) |
|
Samsung PM1743 |
5 |
U.2 |
Enterprise |
1,920 to 15,360GB |
High-Performance Computing (HPC) |
|
Samsung PM1733A |
4 |
U.2 |
Enterprise |
1,920 to 15,360GB |
Read Intensive – Random Performance |
|
Solidigm D5-P5336 |
4 |
U.2, E3.S |
Datacenter |
7.68 to 61.44TB |
Read Intensive – Sequential Performance |
Installation and storage configurations
NVMe adapters are simple to install. The cards are generally low-profile, and can easily fit into the most compact computing chassis. Switch adapters require nothing aside from physical installation, and are essentially plug-and-play devices. RAID controllers require driver and/or software applications, but much of this is done via a ‘wizard’ installer and requires little input from the administrator.
They do, however, require the use of management and configuration interfaces. As professional solutions this is expected – some IT background is certainly useful, but not necessarily a hard requirement. HighPoint’s WebGUI is user friendly, and appeals to first-time users and veteran administrators alike. Everything is broken down into simple drop-down menus and button clicks. Advanced users will appreciate the finer details, however. The interface provides minute to minute data on each hosted SSD, including S.M.A.R.T. attributes, temperature and even endurance ratings (TBW/DWPD).
As discussed previously, NVMe adapters host NVMe media via cable connectivity. The cables can be connected directly to the NVMe SSDs, or to a specialized computer board known as a storage backplane. More about NVMe cabling solutions
SFF-8639 (with power connector)

The cables for direct-to-SSD configurations typically include power connectors, and each cable supports 2 SSDs. Connector types include SFF-8639 (U.2 and U.3 media) and SFF-TA-1002 (for E3.S SSDs).
Backplanes are used by mobile racks and storage chassis. One side of the backplane provides connectors for the SSDs (generally 2.5” drive trays and SFF-8639).

Cable designed for backplane connectivity support a wide range of connector types including MCIO 8i (for Gen4 and Gen5 media), SFF-8654 (Gen4 media), SFF-8643 (Gen3 media), and OCulink (SFF-8611/SFF-8612 for Gen3 and Gen4 media).
Use-cases and applications
As discussed previously, NVMe adapters were designed to host a large number of 2.5” NVMe SSDs (U.2/U.3/E3.S) which are designed for enterprise server environments. Datacenters, large-scale hosting and virtualization solutions, enterprise business servers, and edge servers are the primary targets. Such applications require reliable, easily-serviced high-density storage solutions capable of accommodating a variety of workflows.
Specialized industrial workstations that require high-random or mixed RW performance characteristics and a high level of storage capacity can reap huge rewards from an NVMe adapter-based storage solution.
RAID adapters provide administrators with a great deal of flexibility due to a rich feature set and fault-tolerance (data redundancy). HighPoint’s Rocket 7628A can host bootable RAID-1 and 10 volumes, which are ideal for SMB file servers, media libraries and even home theater applications.
High-speed data ingestion/data acquisition
As the names suggest, these types of applications require storage solutions capable of rapidly capturing large amounts of incoming data, often ingested/acquired from sensors or cameras. Examples include ML, AI training, driver assistance systems (automotive), and various audio-video platforms (AV) ranging from motion capture solutions to high-resolution security systems. NVMe RAID Adapters are especially adept at these tasks, as RAID-0 striping can leverage multiple 2.5” SSDs to enhance response times while maximizing transfer performance and capacity.
Data processing/analysis
Applications that rapidly analyze and process data (often from a High-Speed Ingestion system) require high-density storage solutions capable of optimizing transfer and I/O performance; a perfect fit for 2.5” NVMe media. Examples include scientific and engineering simulations, online transaction servers, and medical diagnosis platforms.
Storage archiving
2.5” NVMe media is beginning to rival SAS/SATA drives in terms of capacity, and the speed advantage is obvious. For this reason, U.2, U.3 and E3.S media is increasingly used to upgrade data archives, asset libraries, and large-scale cloud-computing services. NVMe adapters can leverage large banks of 2.5” media to provide fast (60+GB/s) and dense (nearly 5PB) storage via a single PCIe slot, and are a natural fit for such applications. NVMe Pro-Class/RAID adapters RAID-1 and -10 capability can be used to enhance data security and reliability of data archives.
RAID adapters offer more flexibility when it comes to use-cases, due to a rich feature set and fault-tolerance (data redundancy). HighPoint’s Rocket 7628A can host bootable RAID-1 and -10 volumes, which are for SMB file servers, media libraries and even home theater applications. Customers could opt for a direct-to-SSD cabling solution for 4 to 8 SSDs. While pricey compared to many AIC solutions, enterprise reliability, speed and massive storage capacity make for a worthy investment.
Maximizing storage potential
In summary, an NVMe adapter can maximize the potential of your storage infrastructure. Whether you’re looking to enhance performance, increase capacity, or ensure data reliability, NVMe adapters provide a wealth of features and capabilities that enable them to rapidly adapt to a wide range of platforms and applications. The robust enterprise-grade material, design and construction facilitate seamless integration and enhance field serviceability, making them an ideal solution for data-intensive AI, ML and LLM server and workstation environments.
By incorporating NVMe adapters into your system, you’re not just adding storage; you’re unlocking new possibilities for data management, performance optimization, and future growth. Embrace the future of storage with NVMe adapters and ensure your infrastructure is ready for the demands of tomorrow’s data-driven world.














 Subscribe to our free daily newsletter
Subscribe to our free daily newsletter


