IDC MarketScape: WW Scale-Out File-Based Storage 2019 Vendor Assessment
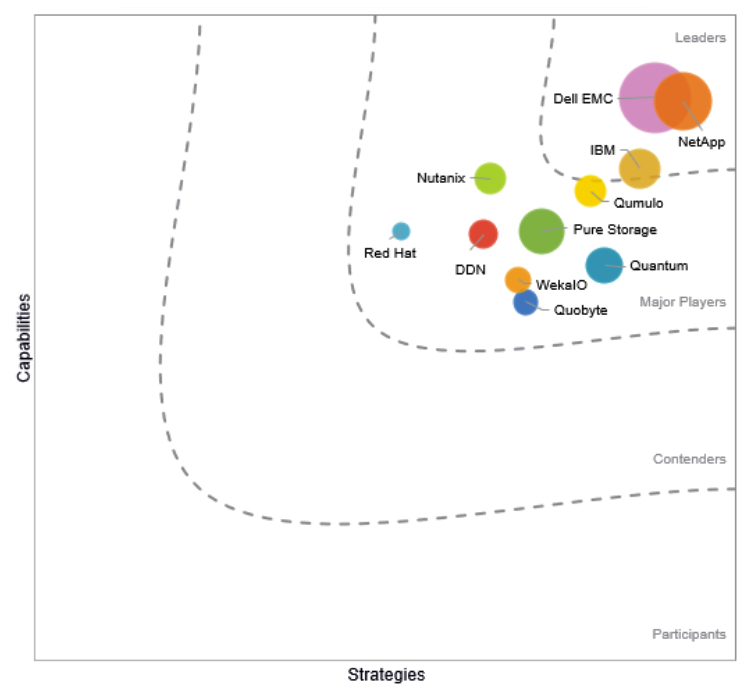
On top right: Dell EMC, NetApp, IBM and Qumulo
This is a Press Release edited by StorageNewsletter.com on December 24, 2019 at 2:17 pm![]() Here is an abstract of a report, IDC MarketScape: Worldwide Scale-Out File-Based Storage 2019 Vendor Assessment ($15,000), written By Amita Potnis, research director, infrastructure systems, platforms and technologies group, IDC Corp.
Here is an abstract of a report, IDC MarketScape: Worldwide Scale-Out File-Based Storage 2019 Vendor Assessment ($15,000), written By Amita Potnis, research director, infrastructure systems, platforms and technologies group, IDC Corp.
IDC classifies file-based storage (FBS) platforms as part of the scale-out file- and object-based storage (FOBS) market segment.
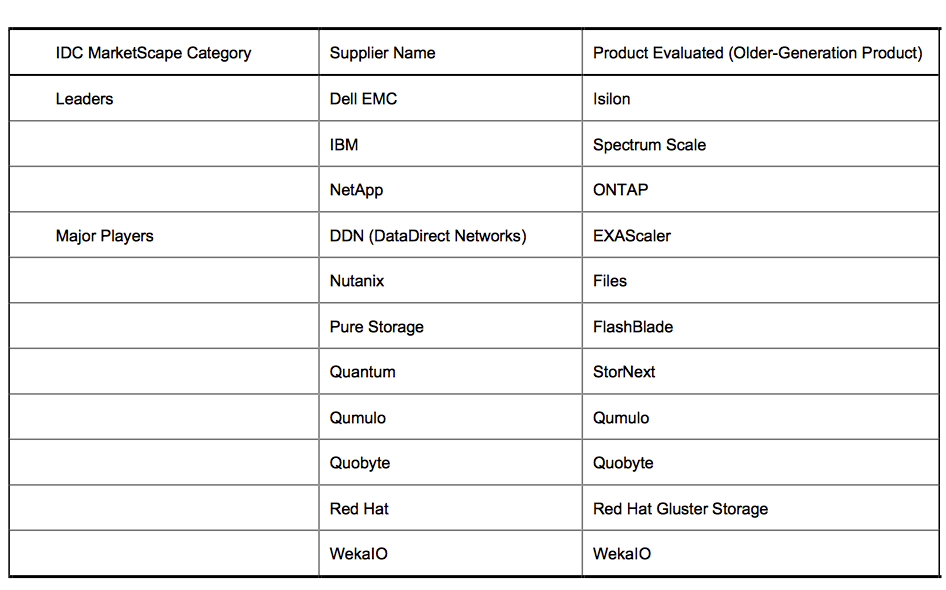
List of players and their classification
“A new digitized world demands an infrastructure that is extremely scalable and flexible in terms of delivery models and supports new high-performant uses cases such as analytics and content delivery,” said Potnis. “FBS platforms hold the promise and the potential to support end users along this path of digitization. In this competitive market, vendors offering FBS platforms with the most compelling value proposition via a long-term strategy, research and development plan, and flexible delivery models will survive.”
Scale-out FOBS refers to FOBS solutions that use a distributed data placement mechanism to span multiple independent server hosts or controllers while presenting a single data access namespace. Such architectures are also called shared nothing (or shared data) architectures. Such architectures allow for flexible scalability in performance and capacity independent of each other using commodity components. Data sharing and distribution mechanisms (such as local and geographic replication and local and distributed erasure coding) account for one or more concurrent component failures. Scale-out FOBS solutions are made up of two variants: scale-out FBS solutions and scale-out FBS solutions.
There are two principal differences between the two types: how data is organized and how data is accessed.
Scale-out FBS solutions use distributed file systems with hierarchical structures to organize and store data. These structures are akin to mechanisms used by monolithic file systems, which in most cases, follow a root directory (folder) and inverted tree structure. In contrast, scale-out FBS solutions use flat structures to organize data. Such structures are higher-level structures in which data is often organized using an “account, container, and object” approach wherein “objects” are analogous to “files” in FBS solutions. Accounts, containers, and objects are referenced by a metadata repository that stores and manages attributes of data stored in that structure.
The level at which FBS solutions operate varies from platform to platform. Many FBS solutions operate on a per object level (i.e., allow each object to be treated independently, as far as policy management is concerned), whereas others operate at a container or account level (i.e., only allow policies to be applied at a container or account level). Several FBS solutions also leverage NoSQL databases as metadata repositories and persistent data stores (instead of storing chunks in the file systems).
Read also:
NetApp (or Isilon?) Leader in WW Scale-Out File-Based Storage in 2012
For IDC
January 29, 2013 | Press Release
Isilon Leader in Scale-Out File-Based Storage WW Market – IDC
Beating IBM and NetApp
by Jean Jacques Maleval | January 18, 2013 | News














 Subscribe to our free daily newsletter
Subscribe to our free daily newsletter


