Elastic Stack V6.7 With Cross-Cluster Replication
Enables cross-datacenter replication, geographically located data, and customizable data replication strategies.
This is a Press Release edited by StorageNewsletter.com on April 11, 2019 at 2:34 pmElastic N.V., the company behind Elasticsearch and the Elastic Stack, announced the availability of cross-cluster replication (CCR) in version 6.7 of the Elastic Stack.
Click to enlarge
CCR enables native replication, data between Elasticsearch clusters, whether they are located in the same datacenter or across the world.
Cross-datacenter replication has been a requirement for mission-critical applications on the Elastic Stack and was previously solved with additional technologies. With its latest release, no additional technologies are needed to replicate data across datacenters, geographies, or Elasticsearch clusters.
“Cross-cluster replication in Elasticsearch has been the most asked-for feature by our cstomers, who have been putting more an more business-critical data into their Elasticsearch clusters,” said Shay Banon, founder and CEO, Elastic. “Built-in cross-cluster replication helps solve for DR, geo data locality, and centralized data location. It is a critical step in Elasticsearch’s evolution as a data store.“
Click to enlarge
The native cross-cluster replication feature is scalable, and reliable and enables a variety of mission-critical use cases for Elasticsearch and the Elastic Stack.
-
DR/HA: Tolerance to withstand a datacenter or region outage has become a requirement for many mission-critical applications. Replicating data across Elasticsearch clusters ensures that if a cluster is unavailable due to a datacenter or infrastructure outage, one or more copies of the data are available in additional locations to ensure BC.
-
Data locality/geo-proximity: CCR can be used to replicate data from a central location to geographically distributed locations to maintain copies of data that are closer to end users. For example, a product catalog or reference data set may be replicated to 20 or more datacenters around the world to minimize the distance between the data and the end user. Another example of geographically replicating data may be a stock trading firm with offices in London, UK and New York. All trades in the London office are written locally and replicated to the New York office, and all trades in the New York office are written locally and replicated to London. Both offices then have a global view of all trades.
-
Centralized reporting: Replicating data from a large number of dispersed clusters back to a centralized reporting cluster is another valuable use case for CCR. This is useful when it may not be efficient to send cross-cluster queries across a large network. For example, a large global bank may have 100 Elasticsearch clusters around the world, each within a different bank branch. CCR can be used to replicate events from all 100 banks around the world back to a central cluster where they can be analyzed and aggregated locally.
Prior to Elasticsearch 6.7.0, these use cases could be partially addressed with third-party technologies. These technologies were cumbersome, carried a lot of administration overhead, and had drawbacks. With CCR natively integrated into Elasticsearch, users are freed of the burden and drawbacks of managing complicated solutions and also enjoy additional advantages that are not available in existing workarounds (e.g., comprehensive error handling). CCR includes both APIs within Elasticsearch and UIs in Kibana for managing and monitoring replication jobs.
The CCR feature in Elasticsearch is designed and architected with government-grade security controls. All replicated data is encrypted in transit across Elasticsearch clusters, and specific access controls can be specified at the cluster, index, document, or field level. Furthermore, CCR bakes in support for centralized authentication systems, which is a requirement for some organizations.
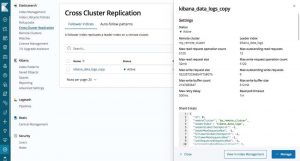
Replication management and administration are important to ensure CCR architectures are correctly configured and working as designed.
The company has released a management and monitoring UI within Kibana specifically for Elasticsearch CCR. Connections across Elasticsearch clusters can be configured and monitored and data replication can be initiated all with a few clicks.
Resources:
Cross-cluster replication blog
Getting started with cross-cluster replication
Elasticsearch reference documentation













 Subscribe to our free daily newsletter
Subscribe to our free daily newsletter

