R&D: Dual-Functional Nanoscale Devices Using Phase-Change Materials
Reconfigurable perfect absorber with nonvolatile resistance-change memory characteristics
This is a Press Release edited by StorageNewsletter.com on February 20, 2019 at 2:09 pmApplied Sciences has published, in special issue Advanced Applications of Phase Change Materials, an article written by Niloufar Raeis-Hosseini, Department of Chemical Engineering, Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH), Pohang 37673, Korea, and Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Imperial College London, London SW7 2AZ, UK, and Junsuk Rho,Department of Chemical Engineering, Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH), Pohang 37673, Korea, and Department of Mechanical Engineering, Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH), Pohang 37673, Korea, and National Institute of Nanomaterials Technology (NINT), Pohang 37673, Korea.
Click to enlarge
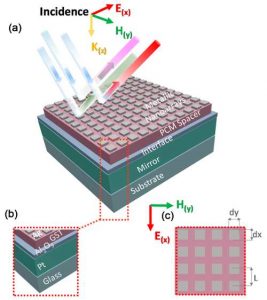
Abstract: “Integration of metamaterial and nonvolatile memory devices with tunable characteristics is an enthusing area of research. Designing a unique nanoscale prototype to achieve a metasurface with reliable resistive switching properties is an elusive goal. We demonstrate a method to exploit the advantages of a phase-change material (PCM) as a metamaterial light absorber and a nanoscale data storage device. We designed and simulated a metamaterial perfect absorber (MPA) that can be reconfigured by adjusting the visible light properties of a chalcogenide-based PCM. The suggested perfect absorber is based on a Ge2Sb2Te5 (GST) film, and is tuned between two distinct states by heat treatment. Furthermore, we fabricated and characterized a resistive switching memory (ReRAM) device with the same features. The MPA/ReRAM device with a conventional metal/dielectric/metal structure (Ag/GST/Al2O3/Pt) consisted of arrays of Ag squares patterned on a GST thin film and an alumina-coated Pt mirror on a glass substrate. Based on the numerical data, amorphous GST showed perfect absorbance in the visible spectrum, whereas, crystalline GST showed broadband perfect absorbance. The fabricated ReRAM device exhibited uniform, bidirectional, and programmable memory characteristics with a high ON/OFF ratio for nonvolatile memory applications. The elucidated origin of the bipolar resistive switching behavior is assigned to the formation and rupture of conductive filaments“.
This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited (CC BY 4.0).














 Subscribe to our free daily newsletter
Subscribe to our free daily newsletter


