Windows 10 and Reserved Storage: Reserving Disk Space to Keep Windows 10 Up to Date
Starting with next major update, making few changes to how Windows 10 manages disk space
This is a Press Release edited by StorageNewsletter.com on January 17, 2019 at 2:06 pm By Jesse Rajwan, program manager, Microsoft Corp., on blog of Windows and Windows Server storage engineering teams
By Jesse Rajwan, program manager, Microsoft Corp., on blog of Windows and Windows Server storage engineering teams
Windows Insiders: To enable this feature now, see the last section ‘Testing out Storage Reserve’ and complete the quest
Starting with the next major update we’re making a few changes to how Windows 10 manages disk space. Through reserved storage, some disk space will be set aside to be used by updates, apps, temporary files, and system caches. Our goal is to improve the day-to-day function of your PC by ensuring critical OS functions always have access to disk space.
Without reserved storage, if a user almost fills up her or his storage, several Windows and application scenarios become unreliable. Windows and application scenarios may not work as expected if they need free space to function.
With reserved storage, updates, apps, temporary files, and caches are less likely to take away from valuable free space and should continue to operate as expected. Reserved storage will be introduced automatically on devices that come with version 1903 pre-installed or those where 1903 was clean installed. You don’t need to set anything up – this process will automatically run in the background. The rest of this blog post will share additional details on how reserved storage can help optimize your device.
How does it work?
When apps and system processes create temporary files, these files will automatically be placed into reserved storage. These temporary files won’t consume free user space when they are created and will be less likely to do so as temporary files increase in number, provided that the reserve isn’t full. Since disk space has been set aside for this purpose, your device will function more reliably. Storage sense will automatically remove unneeded temporary files, but if for some reason your reserve area fills up Windows will continue to operate as expected while temporarily consuming some disk space outside of the reserve if it is temporarily full.
Windows Updates made easy
Updates help keep your device and data safe and secure, along with introducing new features to help you work and play the way you want. Every update temporarily requires some free disk space to download and install. On devices with reserved storage, update will use the reserved space first.
When it’s time for an update, the temporary unneeded OS files in the reserved storage will be deleted and update will use the full reserve area. This will enable most PCs to download and install an update without having to free up any of your disk space, even when you have minimal free disk space. If for some reason Windows update needs more space than is reserved, it will automatically use other available free space. If that’s not enough, Windows will guide you through steps to temporarily extend your hard disk with external storage, such as with a USB stick, or how to free up disk space.
How much of my storage is reserved?
In the next major release of Windows (19H1), we anticipate that reserved storage will start at about 7GB, however the amount of reserved space will vary over time based on how you use your device. For example, temporary files that consume general free space today on your device may consume space from reserved storage in the future. Additionally, over the last several releases we’ve reduced the size of Windows for most customers. We may adjust the size of reserved storage in the future based on diagnostic data or feedback. The reserved storage cannot be removed from the OS, but you can reduce the amount of space reserved. More details below.
Following two factors influence how reserved storage changes size on your device:
-
Optional features. Many optional features are available for Windows. These may be pre-installed, acquired on demand by the system, or installed manually by you. When an optional feature is installed, Windows will increase the amount of reserved storage to ensure there is space to maintain this feature on your device when updates are installed. You can see which features are installed on your device by going to Settings>Apps>Apps & features>Manage optional features. You can reduce the amount of space required for reserved storage on your device by uninstalling optional features you are not using.
-
Installed Languages. Windows is localized into many languages. Although most of our customers only use one language at a time, some customers switch between two or more languages. When additional languages are installed, Windows will increase the amount of reserved storage to ensure there is space to maintain these languages when updates are installed. You can see which languages are installed on your device by going to Settings>Time & Language>Language. You can reduce the amount of space required for reserved storage on your device by uninstalling languages you aren’t using.
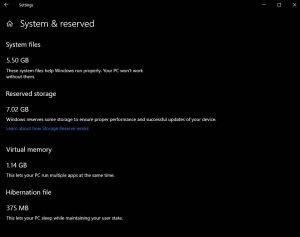
Click to enlarge
Follow these steps to check the reserved storage size: Click Start > Search for ‘Storage settings’ > Click “Show more categories” > Click ‘System & reserved’ > Look at the ‘Reserved storage’ size.
Testing out reserved storage
This feature is available to Windows Insiders running Build 18298 or newer.
-
Step 1: Become a Windows Insider.
The Windows Insider Program brings millions of people around the world together to shape the next evolution of Windows 10. Become an Insider to gain exclusive access to upcoming Windows 10 features and the ability to submit feedback directly to Microsoft Corp.’s engineers. Learn how to get started: Windows Insiders Quick Start -
Step 2: Complete this quest to start using this feature.
Aaron Lower, program manager, Microsoft, contributed to this post.













 Subscribe to our free daily newsletter
Subscribe to our free daily newsletter

