Novel Selector Enables High Density Non-Volatile Memory Chips
From Data Storage Institute A*STAR
This is a Press Release edited by StorageNewsletter.com on August 6, 2015 at 2:42 pmIn this article, the DSI (Data Storage Institute) team has demonstrated a novel selector based on doped chalcogenide material. This novel selector shows nearly ideal selector performances and exhibits comparable or even better performance than the state-of-art selectors demonstrated by other industry players.
By Hongxin Yang, Minghua Li, Wei He, and Yu Jiang, Non-Volatile Memory Division, Data Storage Institute, Agency for Science Technology and Research (A*STAR), Singapore.
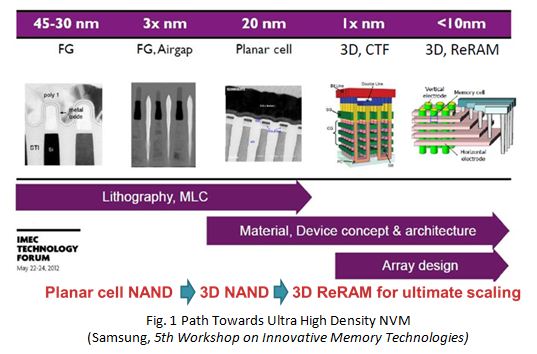
Consumer electronics products, including cell phones, digital cameras, iPads, wearable electronics and notebooks, are supporting the growing demand for non-volatile memories (NVMs). Currently, NAND flash memory dominates the NVM market because of its high density and low cost chips compared to other NVM candidates. The flash memory has evolved from floating gate (FG) to charge trapping (CTF) type and from planar structure to 3D vertical structure. However, flash memory is facing severe scalability limitations. Beyond 10 nm technology node, the intrinsic limitation of electron tunneling remains a problem for the Flash memory technology.
Alternative NVMs other than Flash memory are in high demand to boost the NVM industry. Generally, four technologies have been widely investigated: Ferroelectric Random Access Memory (FeRAM), Spin Torque Transfer Magnetoelectric Random Access Memory (STT-MRAM), Phase Change Random Access Memory (PCRAM), and Resistive Random Access Memory (RRAM). RRAM technology is an emerging candidate for next-generation NVM application due to its simple structure, low programming voltage (<3 V), fast switching speed (<10 ns), high on/off ratio (>103), excellent scalability (<10 nm), good endurance (106-1012 cycles) and great compatibility with the silicon CMOS technology. 3D integration of RRAM at back-end-of-line (BEOL) is a promising approach for enabling an ultra-high density memory architecture featuring 4F2/N cell size (N is the 3D layer number) as shown in Fig. 1.
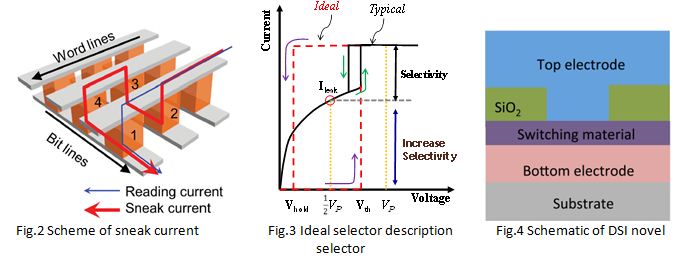
3D RRAM array has the advantages in low fabrication cost and scaling since it uses vertical NAND like structure where multi-layers are formed simultaneously. However, 3D RRAM array needs a selector device connected to RRAM device in series so as to avoid false reading of the RRAM cell due to the sneak current as indicated in Fig. 2. Besides, as the array size increases, large amount of leakage current will cause high power consumption issue. In order to eliminate the sneak path and reduce the power consumption, a high performance selector is needed for emerging two-terminal memory cells. An ideal selector as shown in Fig. 3 should have low leakage current, low holding voltage Vhold, large hysteresis window and fast speed. Currently, there are several selector candidates, including Samsung developed Ovonic Threshold Switch (OTS), Hynix developed Mott effect based selector, IBM developed Mixed-Ionic-Electronic-Conduction (MIEC) based selector, and Cross-bar developed Field-Assisted-Superlinear-Threshold (FAST) Selector. OTS, MIEC and FAST selectors show overlapping IV curves between the forward and backward voltage sweep, which means no holding voltage exists. A partial reset might occur during programming because of the voltage-drop competition between the selector and the memory devices. Hence, a selector with low on-state holding voltage (Vhold) is desired.
In DSI, we have demonstrated a novel selector based on doped chalcogenide material (As seen in Fig. 4). In order to achieve better selector performance, proper material preparation and film deposition is developed. By proper structure engineering, this novel selector shows nearly ideal selector performances (as shown in Fig.5 and Fig.6) with >107 on/off ratio, 0.2 V holding voltage, 10 pA off-state leakage current, sharp on-switch slope of 7 mV/dec, <10 ns turn on speed, >109 endurance, >1.6 MA/cm2 on current density, good scalability, good thermal stability, and large hysteresis window.
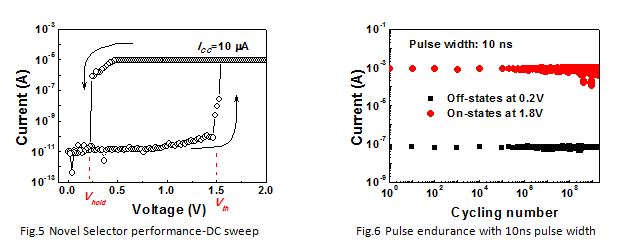
This novel selector exhibits comparable or even better performance than the state-of-art selectors demonstrated by Samsung, IBM, crossbar et al., which indicated our advanced development on this field and also enables the 3D RRAM integration. Our latest results were presented during the last Symposium at VLSI Technology and Circuits 2015 in June.
[Ref.] H.X. Yang et al, VLSI 2015, T9-2














 Subscribe to our free daily newsletter
Subscribe to our free daily newsletter


